Smart pills are a rapidly evolving technology. People are starting to realize that you can put electronics in the human body that are not connected with wires, cords, and catheters. Here is a quick look at some of the amazing technologies that are being developed.
This technology was first introduced for commercial healthcare services in 2000. The most common ingestible sensors are used for imaging, sensing different types of gasses, monitoring medication compliance or absorption of medication, and sensing electrochemical signals.
These are single-use disposable digital capsules that do not require surgical procedures or the administration of anesthesia. The manufacturers develop various products that are customized to function in the different parts of the gastrointestinal tract.
Imaging
Medtronic now owns the PillCam product line for endoscope imaging for the GI tImagingract. Endiatx’s Pillbot is an imaging camera that can move.
Image source: Medtronic
Robotic Endoscope for GI Tract
ANKON Technologies, a Chinese company, manufactures magnetically controlled robotic capsule endoscopes and endoscope control systems.
Image source: ANKON Technologie
Drug Administration
The RaniPill™ capsule, developed by Rani Therapeutics, has a coating that allows it to move through the stomach without being digested but dissolves when it gets to the intestines. This triggers a chemical reaction that inflates a balloon that pushes a needle which, in turn, administers a drug.
Image source: Rani Therapeutics
Monitor Medication
Proteus Digital Health, a Redwood City based company, has developed an ingestible sensor device that allows patients, families, and physicians to measure medication ingestion and adherence patterns. It is currently laying off 300 employees after $500M invested so far. It previously was valued at $1.SB.
Image source: Proteus Digital Health,
Smart Pills Drug Delivery
Inside the body, the robot by Bionaut Labs is magnetically steered to a target to release a precise dose of drugs. This targeted delivery enables precise treatment while minimizing collateral damage to the body, which is a major issue with current cancer treatments such as chemotherapy.
Image source: bionautlabs.com
Gas Sensing
Atmo Biosciences’ gas-sensing capsule electronically measures the concentration of gases in the human gastrointestinal tract which is useful in detecting biomarkers for diagnosis.
Image source: Atmo Biosciences
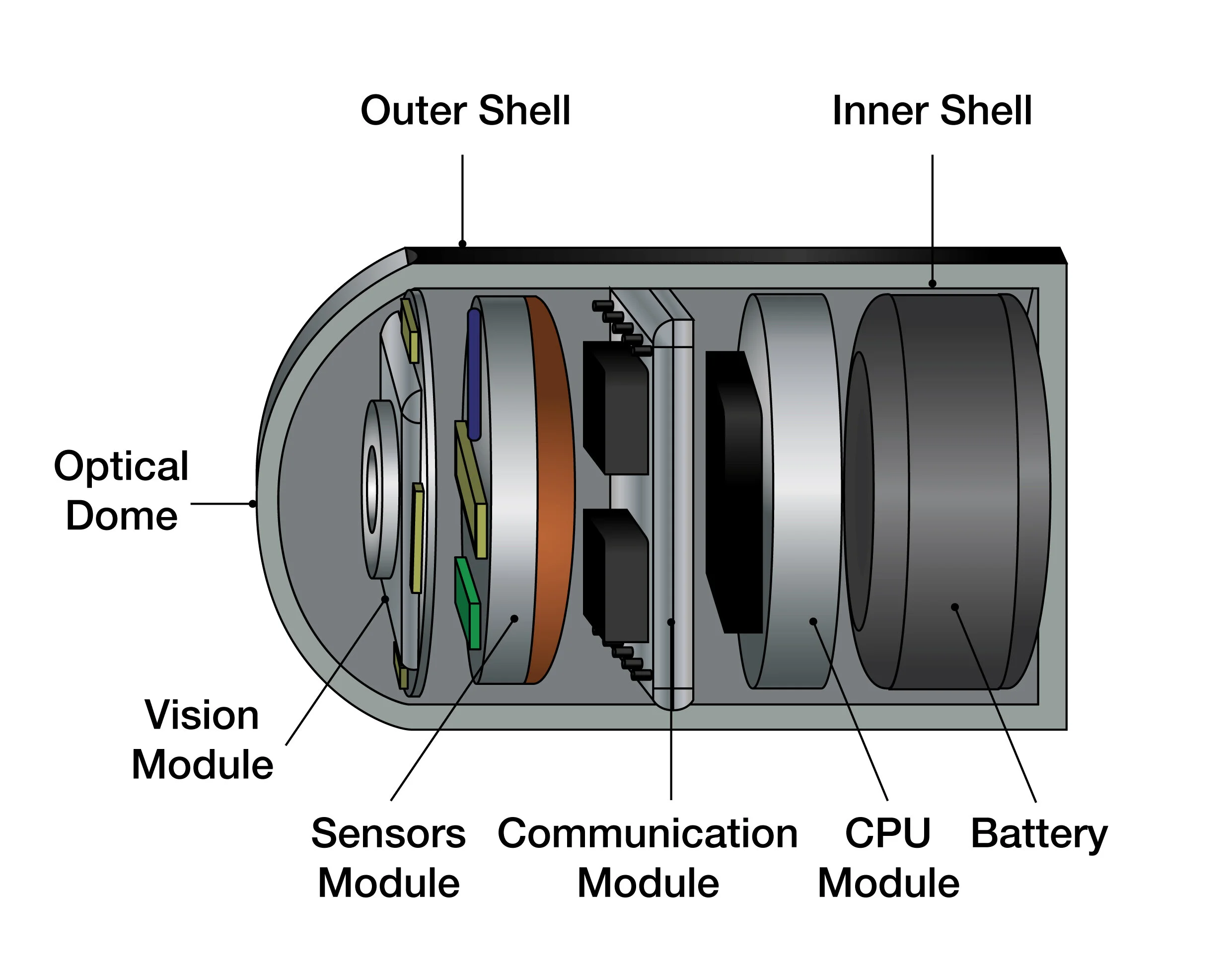
Design Challenges
Image source: Fusion
Size constraint is a significant challenge Radial arrays and linear stacking of disks can be used for mechanical optimization. The environment inside the body also offers challenging design constraints. The materials need to meet biocompatibility and sterilization requirements, but also materials, seals, and coatings need to be resistant to harsh stomach acid. Part of the enclosures may need to be transparent.
Fusion Design provides engineering services and manages the design trade-offs and optimization. We pride ourselves on providing complete solutions using different technical disciplines. Our projects range from small plastic enclosures to large automated robotic systems.